Localization for BLE tag trackers
Learn about the different components of a BLE tag tracking solution and its configuration.
Sometimes the cost of connected trackers doesn't fit the ROI of the customer. For these lower value asset cases, but also for customers who want small trackers, there is the BLE tag tracking solution.
The big difference with the connected trackers is that tag trackers do not directly connect to the internet but need some intermediate
Tags and infrastructure devices
BLE tag tracking is a solution to track the location of assets that always uses at least two devices to properly function:
- BLE Tags: Small BLE tags are attached to an asset. The tags are relatively simple devices that emit a Bluetooth Low Energy identification signal every few seconds. BLE tags are always battery powered.
- Infrastructure: BLE scanning devices: A scanning device performs periodic scans for nearby BLE tags and sends these observed tags to the Sensolus platform. The platform will then register the location of the tagged asset with the location of the scanning devices.
BLE tag tracking is fundamentally different than "connected trackers" because BLE tag is not capable of any network communication and always relies on scanning devices. To emphasize the difference with BLE tags, you can think of connected trackers could also be described as "stand-alone trackers".
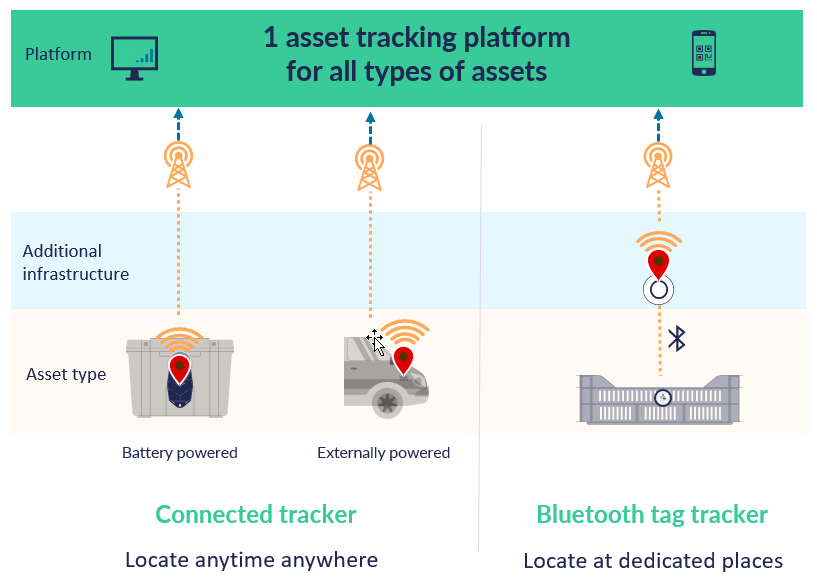
BLE tag tracking is a solution to track assets at specific locations where the scanning devices can be installed. This makes it potentially a good fit for closed loop asset flows. It is not a good solution to locate assets that can move to any location.
The small cost of BLE tags can make it useful to track lower value assets for which otherwise the cost of a more expensive connected tracker would make the solution not cost-effective. On the other hand, the costs of the scanning device infrastructure must also be considered. So, in general, BLE tag tracking makes sense when have a high amounts of lower-value assets, where it is important to know inventory levels at specific locations.
BLE Scanning devices
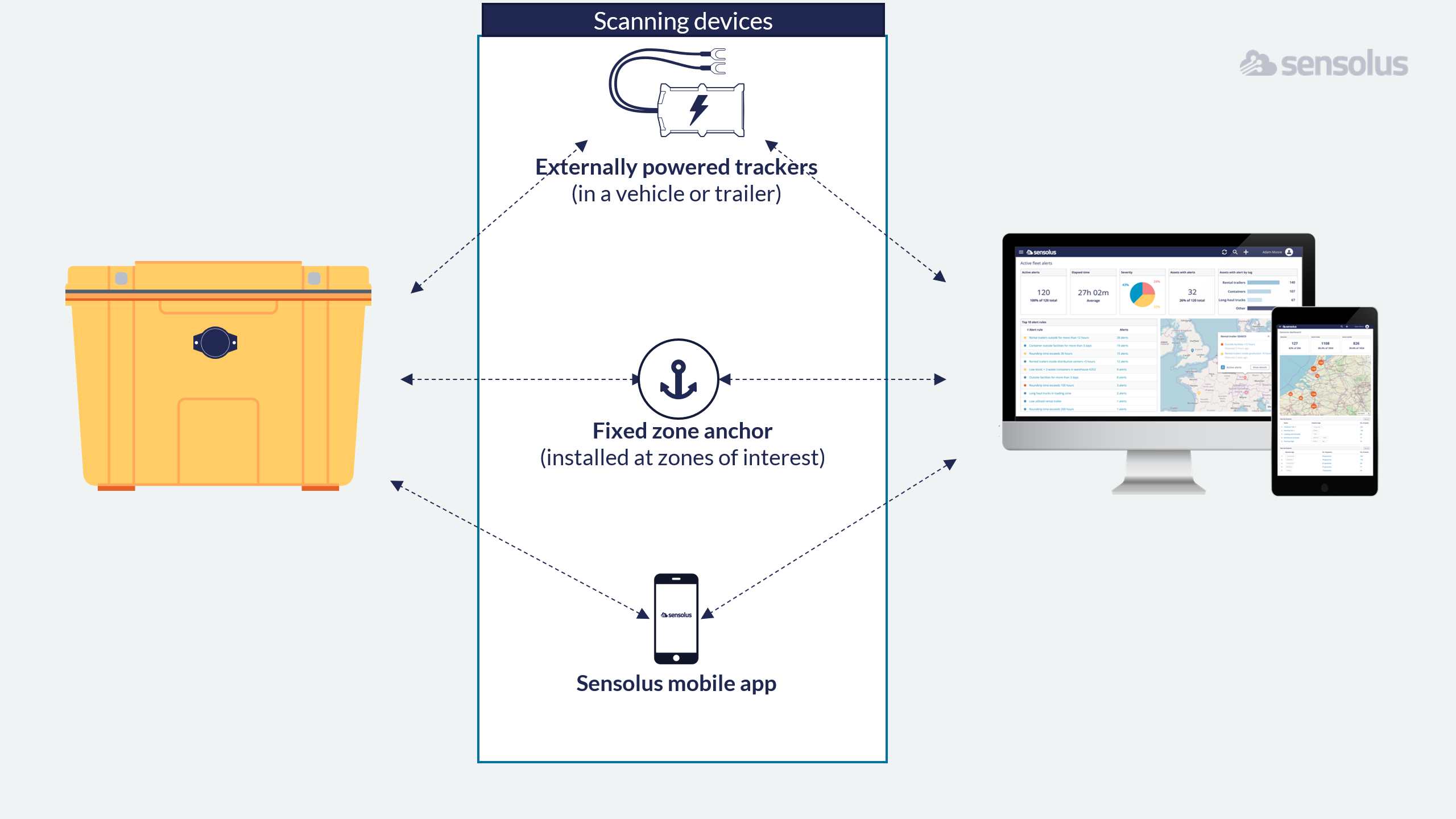
For any Bluetooth tag tracking solution to function properly, there should also be several scanning devices active. These scanning devices listen for the BLE signals emitted by the tags. They keep a list of detected tags in memory, and periodically – for example every 5 minutes – send the list of detected BLE tag IDs to the cloud platform. Since the platform knows the location of scanning devices ; it can update the location of tagged assets to the location of the scanning device.
So, in contrast with the tags, the scanning device should have a way to communicate with the cloud platform. They typically also have a number of more advanced and configurable features, such as listening only for tags of a specific owner, setting the scanning interval and the interval at which to send updates to the platform.When it comes to scanning BLE tags, we can distinguish three types of scanning devices:
- Zone Anchors are scanning devices that are installed at a fixed location -meaning, that they are not moving after installation. “Zone” means that they scan for tags with a certain range. We use “Anchor” because, from the perspective of the business user accessing the platform, we will see the BLE tags as moving– or , in way, ‘docking’ – from one fixed anchor to the other fixed anchor. You might also see that other vendors call this a ‘gateway’ – because they act as the information gateway to the internet. We use the term ‘zone anchor’ because this more accurately describes the purpose, and doesn’t confuse with other network equipment.
- A vehicle trackers – installed in a van or a truck – is also capable of scanning for nearby BLE tags. Note that we also sometimes call them ‘externally powered trackers’ because they are powered by an external power source – being the battery of the vehicle. Since these externally powered trackers are expected to be on the move frequently, they have a GPS/GNSS module so they can self-locate their position . The platform will set the location of the tagged assets equal to the last known GPS/GNSS location of the externally powered tracker.
- Mobile phone with Sensolus app: Finally, consumer mobile phones also have Bluetooth capabilities – and also a GNSS functionality. A mobile phone with the Sensolus app can also scan for nearby BLE tags and report that to the platform. Obviously, this is a lower level of automation compared to the other two scanning device types.
| BLE zone anchor ZA3510 (powered) | BLE zone anchor ZA3510 (battery powered) | Vehicle trackers TRACK 1210 | Sensolus mobile app on Zebra device | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ideal environment | Indoor Controlled |
Indoor-outdoor Controlled |
Drop-off locations Controlled |
Indoor-outdoor |
| Tag gets location from | Location of zone anchor as appointed on the platform | Location of zone anchor as appointed on the platform | GPS in vehicle tracker | GPS in mobile device |
| Positioning accuracy range | ~20m up to 200m | ~20m up to 200m | ~20m up to 200m | ~20m up to 200m |
| Wires needed for installation | Wires for power | No | Yes in trucks to install tracker in the back of the truck. | No |
| Tags scanned at the same time | max. 2000 | max. 2000 | max. 500 | max. 500 |
BLE tag tracking versus BLE geobeacons
At first, it is easy to confuse BLE tag tracking (and BLE zone anchors) with BLE geobeacons. However, geobeacons (Geobeacon localization) are completely unrelated to tag tracking, except that Bluetooth Low Energy signals are used as a technical means to function.