May 24, 2024
Public release notes release 5.6.4
New option in scheduled reports: skip sending empty reports
When users created scheduled reports, sometimes the users don’t want to have the annoyance of receiving report emails that do not have any results. Therefore we added the "do not email report when there are not results" option to the scheduled reports.
Information on the communication operator shown in the platform
The operator that is used by your device to communicate over the network is now also shown in the platform. This can be handy for diagnostic purposes when you have a problem with your tracker.
Optimization of maps: preserve map state
When a user customizes a map (for example, chooses satellite view or certain geolayers to be shown) on the platform it will from now on remember the customization and the map settings are kept for the next login.
Every single map on the platform can be customized and each customization will be kept for the next login. This means the user can configure the asset map in satellite view with coverage maps visible and let the single geozone maps only show street view without extra geolayers.
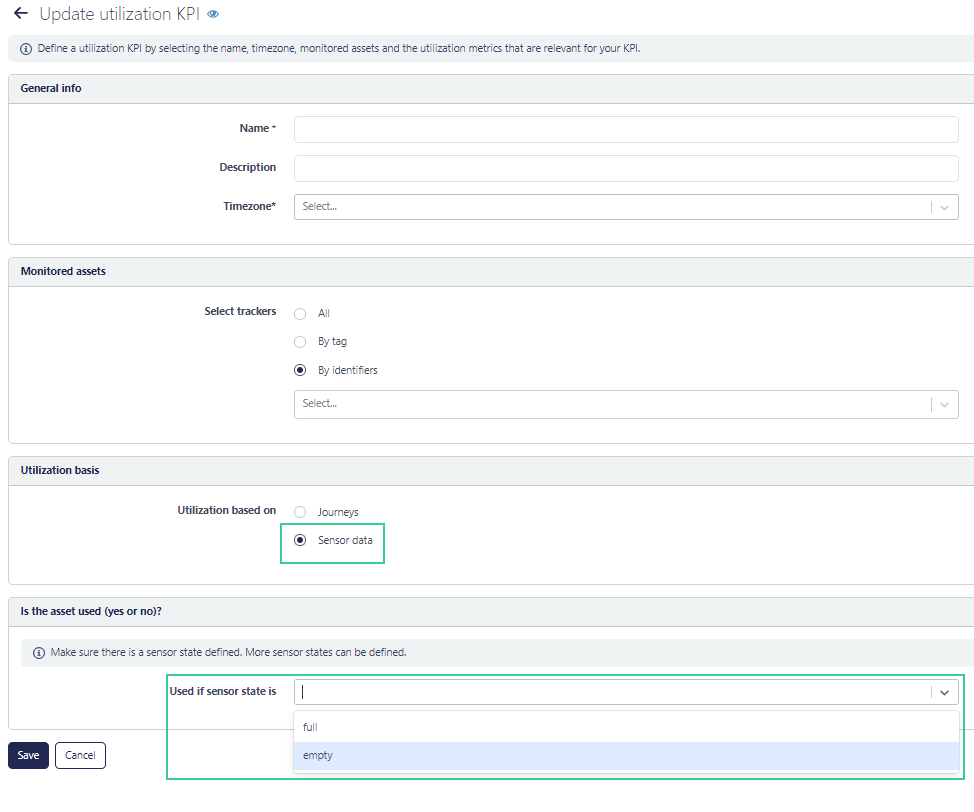
New utilization metric: sensor state
Until now utilization was calculated using location or activity information of the tracker (count of number of journey stops, duration of activity or distance traveled). Now we added sensor information as metric for calculating utilization. The definition of usage is then calculated on the sensor state (for example: "above 40 degrees" for a temperature sensor or "box is open" for orientation sensor or full or empty with a PCR sensor).
Periodic locations in the platform: average different nearby location points to one location
When trackers do periodic location fixes we often get a small spiderweb of locations. Ideally these different locations should all converge to a single best location, however in practice we get the spider and often trackers jumping in an out of a geozone. With this update we converge these different points to a single best position. This is not done on the platform (where you can choose between the compact and all view) but on the edge device itself. With every new location point the average location of the nearby point is calculated with the goal to make the location as accurate as possible.
Improvement to processes
We added the ability to have multiple direct transition rules to the process engine. In addition, it will be possible to assign a process state for a process to a set of trackers in bulk.
Explanation on where a BLE tag gets its location from (now and historically)
BLE tag trackers never get a location by themselves but are dependent of scanning infrastructure to get a location.
Until now the source (GPS, Wi-Fi) of the scanning infrastructure was shown as location source on the tag status page. This was rather confusing.
From now on we add the scanning device from which the location source is used to give a tag a location. This should make the service better understandable for the user.
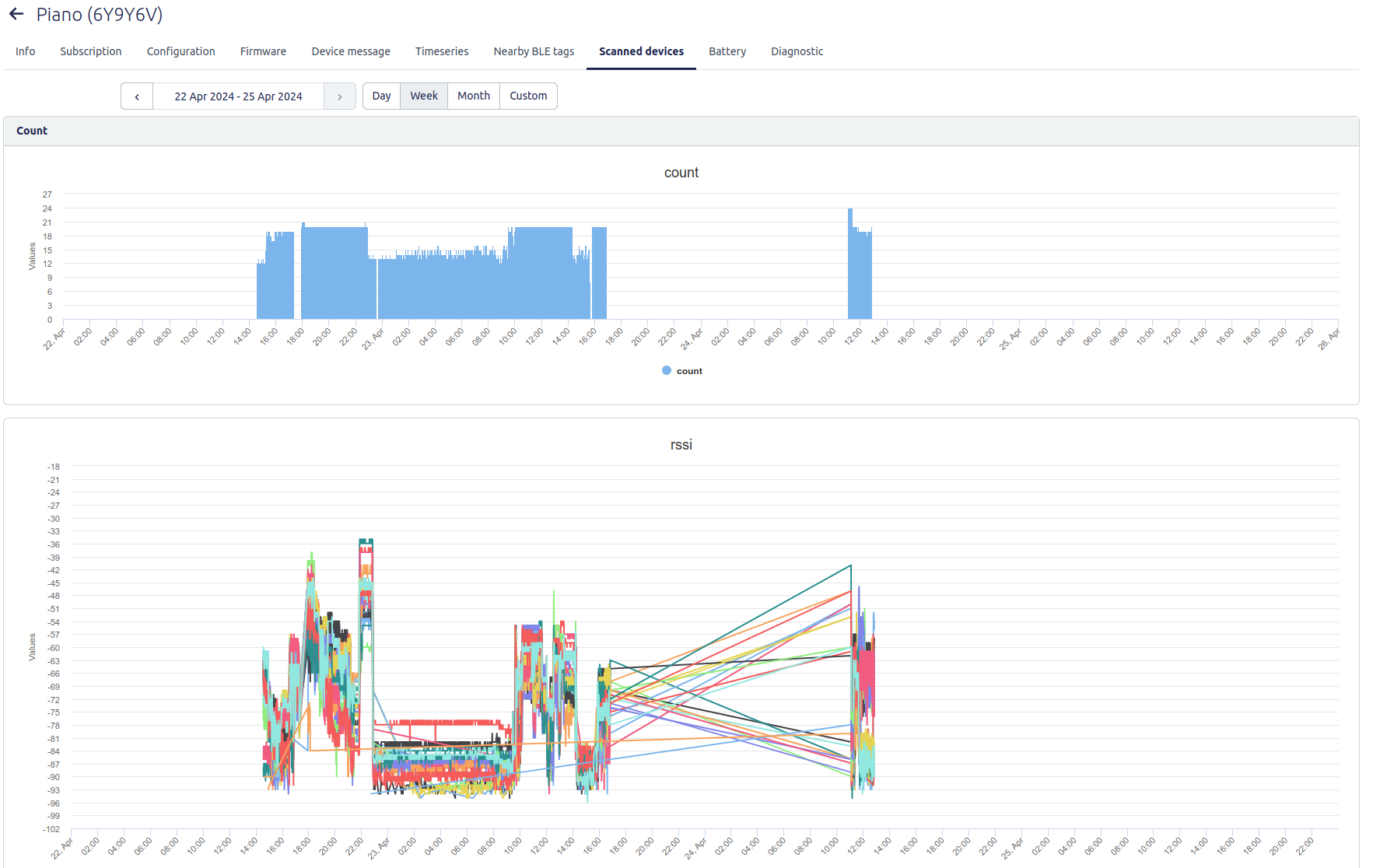
See how many and which tags a zone anchor is scanning
For BLE zone anchors we now show also the tags they are scanning. This interface is mostly interesting when you are running a test with BLE tags.
Go to Admin → Infrastructure → select zone anchor → Select Nearby BLE tags tab.